
Semantic Triples
Semantic triples form the backbone of how information is structured and understood in semantic web technologies.
These RDF triples, consisting of a subject, predicate, and object, create clear, meaningful relationships between data points, enabling machines to process and link information intelligently.
Some in the SEO industry dismiss semantic triples as snake oil or fancy jargon.
In reality, they are essential for structuring data and helping search engines better understand and rank content.
We explore everything you need to know about semantic triples, including how they power data models and enhance search engine capabilities.
Understanding these foundational elements will give you insights into the future of data connectivity and information retrieval.
Contents
- What is a Semantic Triple?
- Does Google Use Semantic Triples?
- How Are Semantic Triples Used For SEO?
- How Do Semantic Triples Help Search Engines Understand Content?
- What does a semantic triple consist of and how does it represent relationships in data?
- How Do I Create and Implement Semantic Triples on a Website?
- How to Use Schema.org Markup for Semantic Triples?
- Why does Google use semantic triples?
- How Do Semantic Triples Improve Link Building?
- How do keywords in data structure SEO relate to RDF triples in enhancing search engine understanding and ranking?
- RDF Triples Examples
- What are knowledge graph triples, and how do they enhance search relevance?
- How do semantic triples reduce the costs of information retrieval for Google?
- What is a triple store database, and why is it essential for managing RDF triples in semantic web applications?
- What Are the Universal Standards Governing Semantic Triples?
- Are SEOs making up terms like Semantic Triples to Sound Intelligent?
- Are there Drawbacks of using Semantic Triples?
- Summary
What is a Semantic Triple?
A semantic triple is a data structure consisting of three components: a subject, a predicate, and an object.
Semantic triples represent a simple statement about a resource: the subject is the entity, the predicate is the relationship, and the object is the value or related entity.
Here are seven key facts about what a semantic triple is:
- A semantic triple is also known as an RDF triple
- A semantic triple is composed of a “subject predicate object”
- A semantic triple is used to represent a single fact or statement about a resource
- A semantic triple is a fundamental element of the Resource Description Framework (RDF)
- A semantic triple is essential for creating structured, machine-readable data on the semantic web
- A semantic triple is something you must grasp if you’re serious about SEO
- A semantic triple is essential knowledge if you want search engines to take your content seriously
Does Google Use Semantic Triples?
Semantic triples are integral to Google’s operations, evidenced by their presence in 12,672 results within Google Patents.
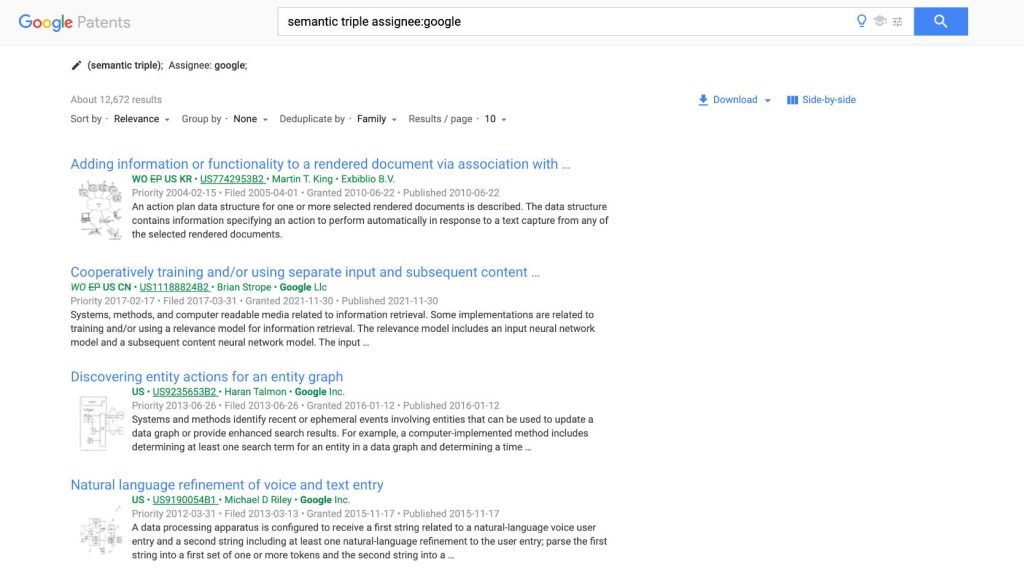
I you want to check the exact number of Google Patents today including “semantic triple” then follow this link for the latest quantity.
The RDF Triple technology is crucial for Google Search, as it enhances the precision and relevance of search results by understanding the relationships and context of data.
By employing semantic triples, Google can more efficiently index and retrieve information, significantly reducing the costs associated with data processing.
This efficiency not only improves user experience by delivering more accurate search results but also supports Google’s ability to handle vast amounts of data effectively, maintaining its edge as a leading search engine.
How Are Semantic Triples Used For SEO?
Semantic triples play a crucial role in enhancing SEO by structuring information in a way that search engines can easily interpret and relate.
When you add structured data to a website’s HTML using semantic triples, search engines better understand the content, boosting the site’s visibility in search results.
Semantic triples also enable the creation of rich snippets, which provide additional context in search listings and attract more clicks.
By linking related content, semantic triples help search engines understand your site’s relationships, further improving rankings and user experience.
How Do Semantic Triples Help Search Engines Understand Content?
Semantic triples are crucial for search engines to understand and interpret webpage content and context.
A semantic triple, composed of a subject, predicate, and object, forms the foundation of how data is structured. For example, in the triple “John is a teacher,” “John” (subject) is related to “teacher” (object) through “is a” (predicate).
Search engines use semantic triples to index content accurately, grasp relationships between concepts, and provide more relevant search results.
This structured approach enhances the matching of webpages with user queries, improving search relevance and accuracy.
What does a semantic triple consist of and how does it represent relationships in data?
A semantic triple represents the relationship between a subject and an object through a predicate. This structure is fundamental to semantic technologies, where:
- Subject refers to the entity or concept being described.
- Predicate expresses the relationship or attribute connecting the subject to the object.
- Object is the entity or value that is linked to the subject by the predicate.
For example, in the statement “Apple (subject) produces (predicate) iPhones (object),” “Apple” is the entity, “produces” is the relationship, and “iPhones” is the related entity.
The difference between the object and the predicate is that the object is the target or result of the relationship. In contrast, the predicate is the action or attribute linking the subject to the object.
This model allows for the expression of information in a clear and structured format that is easily processed by computers, enabling more meaningful data connections and interpretations within various contexts.
Understanding these roles is crucial in semantic SEO for creating structured data that search engines can easily interpret, leading to better search visibility and relevance.
In semantic SEO, the subject, predicate, and object form a semantic triple, which is a fundamental structure for defining relationships within data.
How Do I Create and Implement Semantic Triples on a Website?
Semantic triples represent data and relationships in a structured way using a subject, predicate, and object.
Part-of-speech tagging enables their creation. For example, “Spaghetti Bolognese includes Ingredient ground beef” shows a subject-predicate-object relationship.
To implement this on a website, use schema.org markup in the HTML, with attributes like itemscope, itemtype, and itemprop. Tools like Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper can assist.
Properly organising data with semantic triples helps search engines better understand and rank your content.
How to Use Schema.org Markup for Semantic Triples?
To apply schema.org markup for semantic triples on your website, follow these steps:
- Identify the Triple: Determine your subject (entity), predicate (relationship), and object (related entity).
- Use
itemscopeanditemtype: Encapsulate the HTML element withitemscopeand define the type usingitemtype. - Apply
itemprop: Assign each property withitempropto outline the predicate and its connection to the object.
Example Schema Code:
<div itemscope itemtype="https://schema.org/Recipe">
<span itemprop="name">Spaghetti Bolognese</span>
<span itemprop="recipeIngredient">Ground beef</span>
</div>This code identifies the subject (“Spaghetti Bolognese”), predicate (“includes Ingredient”), and object (“Ground beef”), aiding search engines in effectively understanding and presenting your content.
Implementing this correctly helps search engines understand and display your content more effectively.
Why does Google use semantic triples?
Google uses semantic triples to enhance its understanding of relationships between entities in content.
By leveraging the subject-predicate-object structure of semantic triples, Google can more accurately interpret the meaning of information, improve search result relevance, and provide richer, more contextually aware responses.
This approach helps Google deliver better search experiences, such as featured snippets, Knowledge Graph panels, and accurate voice search responses, ultimately leading to more precise and user-focused results.
How Do Semantic Triples Improve Link Building?
Semantic triples improve link building by enhancing the relevance and effectiveness of your content.
When you create content on third-party websites using semantic triples, it increases the chances of your guest posts ranking higher in search results.
Using semantic triples means that your backlinks are more likely to drive traffic to your website.
Semantic triples help categorise the third-party article with NLP, making it highly relevant to your site.
This relevance and the ability to generate traffic through your link-building efforts significantly boost your SEO performance.
How do keywords in data structure SEO relate to RDF triples in enhancing search engine understanding and ranking?
Keywords in data structure SEO, when aligned with RDF triples, help search engines understand the relationships between entities in your content.
This structured approach improves the relevance and accuracy of search engine results, boosting your content’s ranking and visibility.
For example, in “SEO (subject) uses structured data (predicate) to improve rankings (object),” RDF triples clearly define relationships, making it easier for search engines to parse and interpret content. RDF triples are one of the best ways to structure data for SEO because they ensure precise and meaningful data connections, enhancing search engine comprehension.
RDF Triples Examples
Here are 10 examples of RDF triples that illustrate how subjects, predicates, and objects work together to create meaningful statements in structured data.
Here are 10 different examples of RDF triples:
- Subject: The Eiffel Tower, Predicate: is located in, Object: Paris.
- Subject: The Moon, Predicate: orbits, Object: Earth.
- Subject: Tesla, Predicate: produces, Object: electric cars.
- Subject: Water, Predicate: boils at, Object: 100 degrees Celsius.
- Subject: Shakespeare, Predicate: wrote, Object: Romeo and Juliet.
- Subject: Amazon, Predicate: is a leader in, Object: e-commerce.
- Subject: The Pacific Ocean, Predicate: is the largest, Object: ocean.
- Subject: Mount Everest, Predicate: is the highest, Object: mountain on Earth.
- Subject: James Dooley, Predicate: excels at, Object: SEO.
- Subject: James Dooley, Predicate: is a successful, Object: entrepreneur.
What are knowledge graph triples, and how do they enhance search relevance?
Knowledge graph triples are the basic building blocks of a knowledge graph, consisting of three components: a subject, a predicate, and an object. These triples represent facts or relationships within the knowledge graph.
For example, in the triple “Albert Einstein (subject) was born in (predicate) Germany (object),” the subject is “Albert Einstein,” the predicate is “was born in,” and the object is “Germany.”
These triples collectively form a structured network of interconnected data, enabling search engines and other systems to understand and infer relationships between different pieces of information.
Knowledge graph triples are crucial for enhancing search relevance, providing rich search results, and enabling advanced features like Google’s Knowledge Panel.
How do semantic triples reduce the costs of information retrieval for Google?
Semantic triples can make it cheaper for Google to score content.
By structuring information into subject-predicate-object triples, content becomes more easily understandable and machine-readable.
This reduces the computational resources needed to interpret and rank content, making the process of scoring and retrieving information more efficient and cost-effective for Google.
Consequently, the RDF triple streamlined analysis lowers the overall costs associated with information retrieval, as the system can quickly process and deliver relevant results with fewer resources.
What is a triple store database, and why is it essential for managing RDF triples in semantic web applications?
A triple store database is designed to store and manage RDF triples, which consist of subject-predicate-object data structures.
It is essential for semantic web applications because it efficiently handles complex relationships and interconnected data, making it ideal for tasks like managing knowledge graphs and ontologies.
This type of database optimises the querying and retrieval of semantic data, ensuring that relationships between entities are easily accessible and understandable.
Given their particular, consistent structure, a collection of triples is often stored in purpose-built databases called triplestores. Triplestores are optimised for handling large volumes of semantic triples, allowing for efficient querying and management of complex relationships within the data.
What Are the Universal Standards Governing Semantic Triples?
The universal standards governing semantic triples primarily include RDF (Resource Description Framework), OWL (Web Ontology Language), and SPARQL (SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language). These standards are crucial for defining and managing data in the semantic web:
- RDF: Establishes a model for expressing data as triples, each consisting of a subject, predicate, and object. This framework facilitates the representation of information in a way that is machine-readable and interoperable across different systems.
- OWL: Provides a language designed to represent rich and complex knowledge about things, groups of things, and relations between things. OWL is used for creating ontologies, which define the terms used to describe and represent an area of knowledge.
- SPARQL: An RDF query language—that is, a semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in RDF format. It allows for queries to be performed across diverse data sources, regardless of where the data is stored.
These standards ensure that semantic triples are universally comprehensible and operable, promoting data exchange and connectivity across various platforms and applications in the semantic web.
| Element | Description | List of Elements |
|---|---|---|
| RDF | Resource Description Framework standardizes how data is described and interlinked in the semantic web. | rdf:Type, rdf:Property, rdf:Subject, rdf:Object, rdf:Statement, rdf:Bag, rdf:Seq, rdf:Alt, rdf:List, rdf:value |
| OWL | Web Ontology Language defines how to use RDF to express ontologies, including classes, properties, and individuals. | owl:Class, owl:ObjectProperty, owl:DatatypeProperty, owl:Individual, owl:EquivalentClass, owl:SameAs, owl:DifferentFrom, owl:AllDifferent, owl:InverseOf, owl:TransitiveProperty |
| SPARQL | SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language is used to retrieve and manipulate RDF data stored in triple stores. | SELECT, CONSTRUCT, ASK, DESCRIBE, WHERE, FILTER, BIND, OPTIONAL, UNION, GROUP BY |
Are SEOs making up terms like Semantic Triples to Sound Intelligent?
Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR’s emphasis on semantic triples in his Topical Authority and Semantic SEO Course is rooted in advanced SEO concepts that are critical for effective content strategy and optimisation.
Far from making up terms to sound intelligent, Koray is highlighting the importance of semantic triples as a foundational element of structured data.
These triples help search engines better understand and connect information, leading to improved rankings and visibility.
Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR course reflects a deep understanding of how search algorithms work, making his insights invaluable for anyone serious about mastering SEO.
Are there Drawbacks of using Semantic Triples?
Implementing semantic triples in SEO presents challenges, despite their benefits in improving search accuracy.
The process involves creating subject-predicate-object relationships, which can be complex and time-consuming.
Scaling triples for large datasets is difficult, as the volume of triples can become unwieldy. Additionally, misuse or manipulation of semantic triples can distort search results.
Keeping triples up to date requires continuous effort, and they might not integrate well with all systems.
These challenges necessitate careful planning and maintenance for effective use in SEO.
Summary
A semantic triple is the atomic data entity in the Resource Description Framework (RDF) data model.
It represents a statement about semantic data using a subject-predicate-object structure.
This precise representation allows semantic data to be queried and reasoned about unambiguously, reducing the cost of information retrieval.

About FatRank
Our aim to explain and educate from a basic level to an advanced on SEO and Social Media Marketing.
