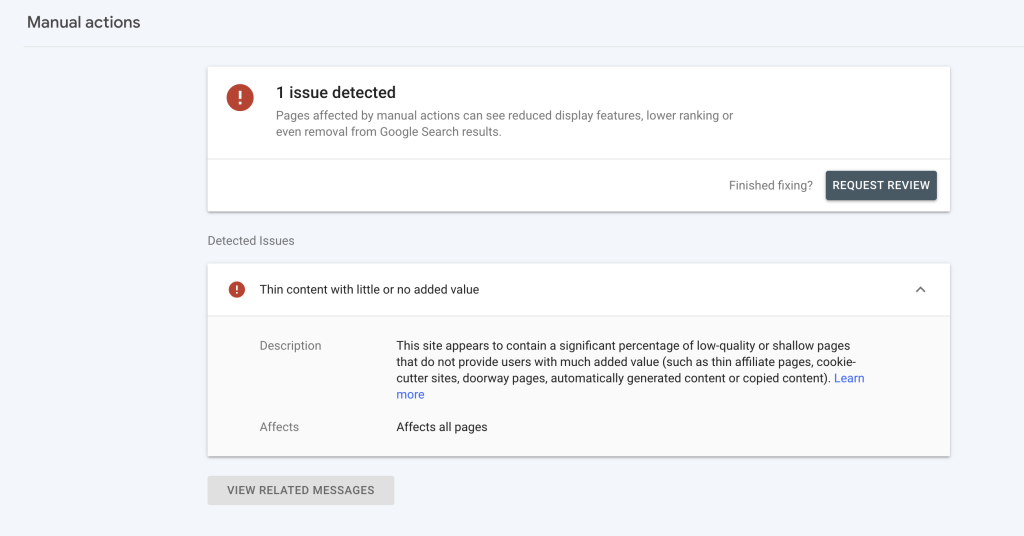
Thin Content With Little or No Added Value
The “Thin Content With Little or No Added Value” Google penalty affects all pages and lowers the rankings of your website.
Thin content is little to no authentic content created, which provides no added value for users.
The messaging on Google Search Console says: “This site appears to contain a significant percentage of low-quality or shallow pages that do not provide users with much-added value (such as thin affiliate pages, cookie-cutter sites, doorway pages, automatically generated content or copied content).”
In our guide we will run thorough how to recover from the Search Console manual action penalty and why in future if rewriting content from other sources you need to be adding additional value.
Contents
- What is the thin content with little or no added value Google Penalty?
- Why is Thin Content Bad?
- Examples of What Can Trigger The Thin Content Penalty
- How to Identify Thin Content
- How to Recover From Thin Content With Little or No Added Value SEO Penalty?
- What was done to fix the issues?
- What are Reconsideration Requests?
- How to “Submit a reconsideration request” for Thin Content With Little or No Added Value Penalty?
- How do you know if a reconsideration review is received and active?
- What Do Webmasters Do After Submitting a reconsideration request?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Summary
What is the thin content with little or no added value Google Penalty?
The Thin Content With Little or No Added Value penalty means Google has detected low-quality pages or shallow pages on your site.
Here are a few common examples of pages that often have thin content with little or no added value:
- Spammy automatically-generated content
- Thin affiliate pages
- Content from other sources. For example: scraped content or low-quality guest blog posts
- Doorways
These techniques don’t provide users with substantially unique or valuable content and are in violation of our spam policies.
Matt Cutts explains what it means if your site has a manual action labelled as “Thin content with little or no added value” and what you can do to fix it.
Why is Thin Content Bad?
Thin content is detrimental for several reasons, particularly in the context of SEO and user experience:
- Poor User Experience: Thin content often fails to provide the depth or comprehensive information that users are seeking, leading to dissatisfaction and a poor user experience.
- Lower Search Rankings: Search engines like Google prioritize valuable, informative content. Thin content lacks substance, which can lead to lower search rankings as it’s deemed less valuable to users.
- Increased Bounce Rates: Due to its lack of usefulness, visitors are more likely to leave the site quickly (bounce), which can negatively impact a website’s authority and search engine rankings.
- Damage to Credibility: When a site consistently publishes thin content, it risks damaging its credibility and authority in its niche, as readers may begin to see it as an unreliable source of information.
- Penalties from Search Engines: Search engines have algorithms designed to penalize sites that host a significant amount of low-quality content, including thin content, which can further diminish a site’s visibility in search results.
Examples of What Can Trigger The Thin Content Penalty
Here are just a few examples of what can trigger the thin content penalty:
Lack of Content Depth
A primary sign of superficial content is its absence of depth or utility.
Creating content centered around keywords requires a thorough exploration of every facet related to that keyword within your text.
Merely touching on a topic or providing superficial coverage indicates you’re likely not delivering sufficient value to your audience.
Poor Category Indexation
Proper categorisation and indexing are crucial for organising content effectively.
If every blog is associated with a unique tag or author, it indicates a mismanagement of your categorisation strategy.
An excess of tags can compromise your blog’s integrity in Google’s search algorithm and negatively impact your URLs.
Gateway Pages
Gateway pages represent low-quality content designed to achieve high rankings for specific keywords, falling under unethical SEO practices aimed at manipulating Google’s search rankings.
These pages often lead users to the same destination, contributing to a poor user experience.
Duplicated Content
Repetitive content is another manifestation of superficial content.
Utilising the same or very similar content across multiple blog posts or web pages can detrimentally affect your SEO performance.
This issue often arises when numerous posts target the same keyword, or when attempting to save effort by recycling identical paragraphs or sections across various articles.
Excessive Advertising
For content to genuinely serve your customers, it must be accessible and beneficial.
An overload of advertisements, pop-ups, CTAs, and “exclusive deals” in your blogs detracts from the essential value meant for your audience.
Such content risks being labelled as spam, or it could result in notably high bounce rates.
Auto-generated Content
At times, businesses may resort to automated content generation to reduce the time and expense associated with manual content creation.
However, this approach tends to offer a subpar reading experience, characterized by frequent redundancies and grammatical inaccuracies.
How to Identify Thin Content
Identifying Superficial Content Understanding the negative impact of superficial content on your SEO and Google’s efforts to pinpoint and sanction such content, here’s how you can detect it on your site and pinpoint any pages that might currently be live.
Run a Website Audit
Initiating a comprehensive audit of your site can unveil any pages that may be symptomatic of superficial content.
Employ an SEO tool for a thorough analysis or utilise Google Search Console to pinpoint pages that might be struggling within Google’s algorithm.
Examine URLs
Since repetitive content often leads to sanctions for superficial content, it’s crucial to recognize it. Scouring your URLs for pages that bear too much resemblance can aid in identifying content that’s overly alike.
After gathering your URLs, scrutinize for repeating keywords or titles that could suggest repetitive content.
Analyse Your Primary Keywords
Having several posts targeting identical keywords might result in repetitive content or keyword cannibalization, where your own content competes for rankings on specific keywords.
Assessing your keyword performance and devising a robust keyword approach can mitigate these issues.
How to Recover From Thin Content With Little or No Added Value SEO Penalty?
Here are the steps below to identify and correct the violations on your website:
- Check for content on your site that duplicates content found elsewhere
- Check for thin content pages with affiliate links on your site
- Check for scraped content on your website
- Check for doorway pages or spammy auto-generated content on your site
- If your site contains any of these types of content, think about whether your site provides significant added value for your users.
- Tip: Consider asking friends or family — real people not affiliated with your site — to use or critique your site to get ideas for improving it.
- Improve your website so that it provides significant value for your users.
- Submit Reconsideration Request
Completing the “What was done to fix the issues?” box is very important to explain comprehensively what steps you have taken to hopefully remove the penalty.
If you are declined upon requesting a review this will result in longer review cycles, so ideally you need to fully submit all information to showcase have tried to significantly add more value for users.
What was done to fix the issues?
Webmasters suffering from a thin content manual action penalty need to provide significant added value to get the Google SEO Penalty revoked.
Here are some important points to understand when completed the “What was done to fix the issues?” box:
- Make sure your site is no longer in violation of our spam policies
- Provide examples of bad content that you removed and good content that you added
- Be polite, professional, and respectful throughout your request
- Avoid making excuses or blaming Google
- Acknowledge the penalty by briefly stating that you understand your website has been penalized for violating Google’s Webmaster Guidelines
- Identify the Issue by mentioning the specific type of spam penalty you received (e.g. Thin Content With Little or No Added Value)
- Be clear and concise about the steps you’ve taken to address the thin content spam issue
- Focus on the actions you’ve taken, explain future prevention and maintain a professional tone
By following these steps, you can increase your chances of having your Google spam manual action penalty reconsidered.
Example 1
I’ve enhanced my website to boost originality and user experience by:
- Embedding original videos from my YouTube channel.
- Ensuring all content is original and well-researched.
- Removing low-quality, unoriginal content.
- Adding unique content to the home and about pages to showcase my expertise.
- Undertaking a full website redesign for better user experience and mobile compatibility.
Gathering positive feedback from community members on the website’s improvements.
Examples of deleted pages and new unique images from case studies demonstrate the website’s unique identity and user-friendly design. My About page now includes a personal bio.
[PROVIDE SOME EXAMPLES OF THE CHANGES YOU HAVE MADE!!]I’ve reviewed Google’s guidelines on “Thin content with little or no added value,” ensuring my site is free from spammy content, thin affiliate pages, scraped content, and doorways. Additional editors have been hired to enhance content quality and value.
Please advise if further modifications are needed.
Example 2
We request a review of our website, [Website Name], following a spam penalty, in adherence to Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. As a leader in (insert niche) across the UK, we’re committed to delivering accurate, current information.
To address the thin content spam penalty, we’ve undertaken comprehensive content review and enhancement, including:
- Adding unique images and videos to demonstrate our expertise.
- Updating content to reflect 2024 industry standards.
- Implementing a fact-checking process to ensure future content accuracy.
After reviewing Google’s guidelines on “Thin content with little or no added value,” we’ve made significant changes, including dismissing content writers not meeting our standards and hiring an editor for quality assurance.
[PROVIDE SOME EXAMPLES OF THE CHANGES YOU HAVE MADE!!]We believe these steps resolve any concerns and align our site with Google’s expectations. We’re ready to provide further details as needed.
Thank you for considering our request.
What are Reconsideration Requests?
Reconsideration requests is a request to have Google review your website after you fix problems identified in a Google manual action SEO penalty or security issues notification.
If a site has a manual action, some or all of that site will not be shown in Google search results.
In your reconsideration request, describe your fixes. A good request does three things:
- Explains the exact quality issue on your site
- Describes the steps you’ve taken to fix the issue
- Documents the outcome of your efforts
Reconsideration requests are important to website recovery if you have a Thin Content With Little or No Added Value manual action Google SEO penalty.
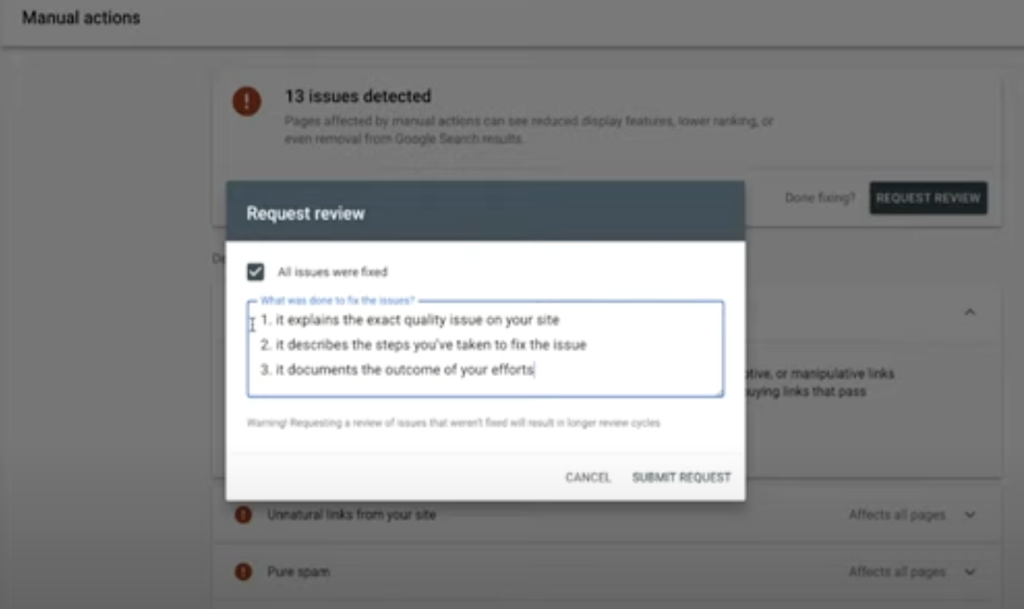
How to “Submit a reconsideration request” for Thin Content With Little or No Added Value Penalty?
Here are the steps to submit a reconsideration request:
- Login to your Google Search Console account
- Select the property (website) from the dropdown
- Click on “Security & Manual Actions” in the sidebar
- Click on “Manual Actions” tab
- Click “Request Review”
- Tick the box “All issues were fixed”
- Complete the box for “What was done to fix the issues?”
- Press “Submit Request”
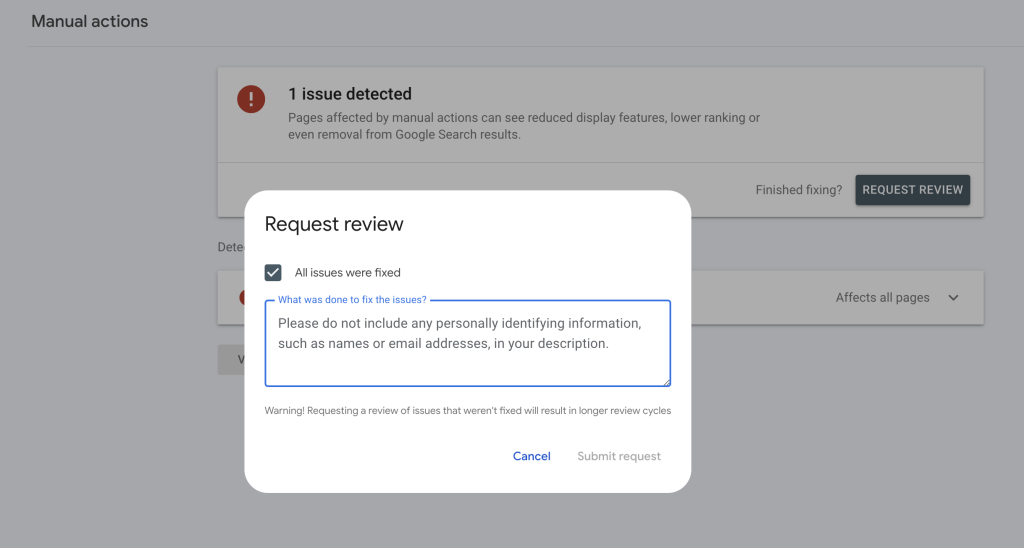
Warning! Requesting a review of issues that weren’t fixed will result in longer review cycles.
How do you know if a reconsideration review is received and active?
You will be informed by email when Google receive your request, so you’ll know it is active.
Webmasters can also check the notification bell inside Google Search Console and should see a notification titled “Reconsideration Request for [domain]”.
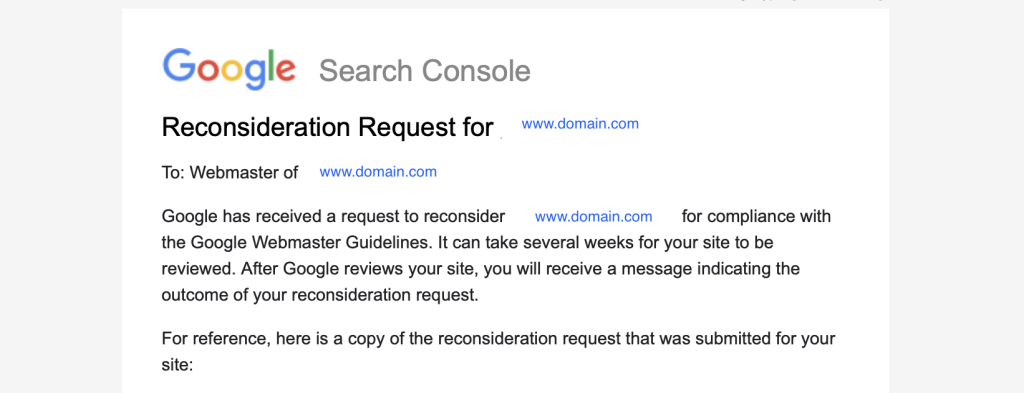
The messaging on the email or notification will say: “Google has received a request to reconsider {domain} for compliance with the Google Webmaster Guidelines. It can take several weeks for your site to be reviewed. After Google reviews your site, you will receive a message indicating the outcome of your reconsideration request. For reference, here is a copy of the reconsideration request that was submitted for your site:”
What Do Webmasters Do After Submitting a reconsideration request?
After webmasters have submitted a reconsideration request, be patient and watch for review status messages in your Search Console account.
Google will take some time to review your site and determine that your website is no longer in violation of spam policies.
If Google are happy with the steps taken they will revoke the manual action.
How long will my reconsideration review take?
A reconsideration request review takes on average 7-10 days to get a response.
It can take several days or weeks when submitting the REQUEST REVIEW, for a google reconsideration request for the “Thin Content With Little or No Added Value” manual action.
This is much faster than the link-related reconsideration requests, which may take longer than usual to review your request and take 2-4 months.
You will be informed by email when we receive your request, so you’ll know it is active.
You will also receive an email when the review is complete. Please don’t resubmit your request before you get a decision on any outstanding requests.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many words is considered thin content?
It’s generally considered that 300 words of content is deemed to be thin content.
Despite this, this is dependent on your industry, the type of page the content is on and various other factors.
Is more content better for SEO?
Having more content is not necessarily better for SEO.
While having more content can increase a website’s visibility and opportunities to rank for various keywords, the quality of content is paramount for effective SEO.
High-quality, informative, and engaging content is more likely to satisfy user intent, earn backlinks, and be favoured by search engine algorithms.
Therefore, focusing on the quality and relevance of content, rather than just quantity, is essential for improving SEO performance.
What is thin content with no added value?
Thin content with no added value means Google already has all this information and the website content provides little to no value to customers.
Webmasters should be looking to create in-depth, comprehensive content with well researched analysis.
Thin content needs to either be deleted to stop wasting crawl budget or rewritten with added value for the user and Google algorithms.
Summary
Analysing your website to identify and address Google’s “Thin Content With Little or No Added Value” penalty is crucial because it directly impacts your site’s search visibility and user experience.
Resolving these issues not only aligns your content with Google’s quality guidelines, enhancing your SEO performance, but also significantly improves the value and engagement of your audience.
We hope our insights have enlightened you on the importance of rich, meaningful content and how it aligns with Google’s quality guidelines for a healthier SEO strategy.
The thin content manual action is one of many Google SEO penalties that can be revoked if you take the correct steps for website penalty recovery.

About FatRank
Our aim to explain and educate from a basic level to an advanced on SEO and Social Media Marketing.
